a custom logger for Python
let’s tune the default logger a bit so he write nice and colored messages.
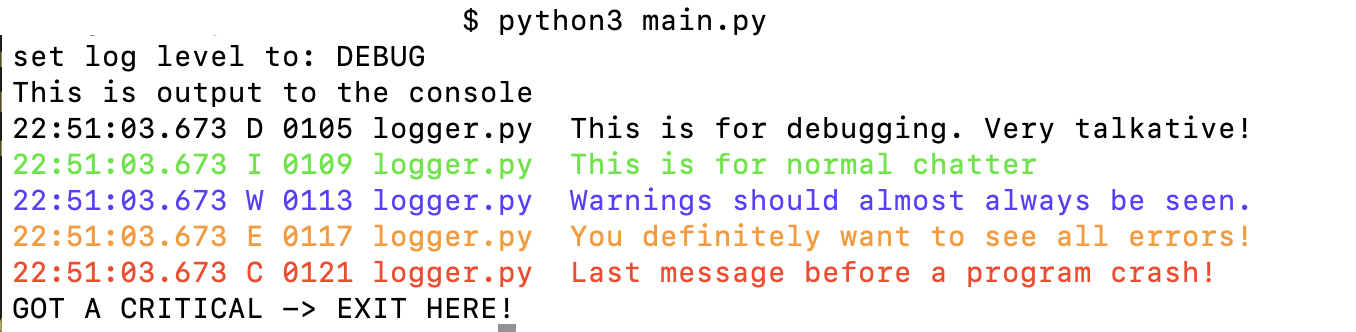
Screenshot
config.py
a little config File …
cat <<'EOF'> config.py
LOGGER_MAX_FILE_LENGTH = 10
EOF
src/logger.py
the logger code in the ‘src’ Folder
mkdir src
cat <<'EOF'> src/logger.py
import logging
import datetime
import sys
from config import *
if isinstance(LOGGER_MAX_FILE_LENGTH, int):
LOGGER_MAX_FILE_LENGTH = str(LOGGER_MAX_FILE_LENGTH)
def get_now() -> str:
#
# choose your format
#
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# 2023-07-16 22:16:15.958
formatted_time_1 = current_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3]
# 22:16:54.471
formatted_time_2 = current_time.strftime("%H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3]
# 22:17:21
formatted_time_3 = current_time.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
return formatted_time_2
class ExitOnCriticalHandler(logging.Handler):
def emit(self, record):
# Unset Color
COLOR = RESET = "\033[0m"
# Debug -> Black
if record.levelno == logging.DEBUG:
COLOR = "\033[0m"
# Info -> Green
elif record.levelno == logging.INFO:
COLOR = "\033[92m"
# Warn -> Blue
elif record.levelno == logging.WARNING:
COLOR = "\033[94m"
# Error -> Orange
elif record.levelno == logging.ERROR:
COLOR = "\033[38;5;208m"
# Critical -> Red
elif record.levelno >= logging.CRITICAL:
COLOR = "\033[91m"
# Custom Line
print(
COLOR
+ "{:} {:} {:04} {:{w}} {:}".format(
get_now(),
record.levelname,
record.lineno,
record.filename,
record.msg,
w=LOGGER_MAX_FILE_LENGTH,
)
+ RESET
)
# Exit on Critical
if record.levelno >= logging.CRITICAL:
logging.shutdown()
print("\033[91m" + "GOT A CRITICAL -> EXIT HERE!" + "\033[0m")
sys.exit()
# Init Logger
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Create and add the custom handler
exit_handler = ExitOnCriticalHandler()
logger.addHandler(exit_handler)
# Set Log Level
def set_log_level(level: str):
# Parse/ Set LogLevel
if level.lower() in ["d", "debug"]:
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
elif level.lower() in ["i", "info"]:
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
elif level.lower() in ["w", "warning"]:
logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
elif level.lower() in ["e", "error"]:
logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
elif level.lower() in ["c", "critical"]:
logger.setLevel(logging.CRITICAL)
# Custom level name mappings, Debug -> D
logging.addLevelName(logging.DEBUG, "D")
logging.addLevelName(logging.INFO, "I")
logging.addLevelName(logging.WARNING, "W")
logging.addLevelName(logging.ERROR, "E")
logging.addLevelName(logging.CRITICAL, "C")
# Functions to Call
def ldebug(msg: str):
logger.debug(msg)
def linfo(msg: str):
logger.info(msg)
def lwarning(msg: str):
logger.warning(msg)
def lerror(msg: str):
logger.error(msg)
def lcritical(msg: str):
logger.critical(msg)
EOF
main.py
the Main File with Argparse to set the Logging Level on Startup
